4.1.1 Electrostatic Adhesion Theory
The electrostatic adhesion theory states that adhesion is a result of the electrostatic forces between the adhesive product and the material to be bonded, where electrons are transferred, forming an electrical double layer that creates attraction.
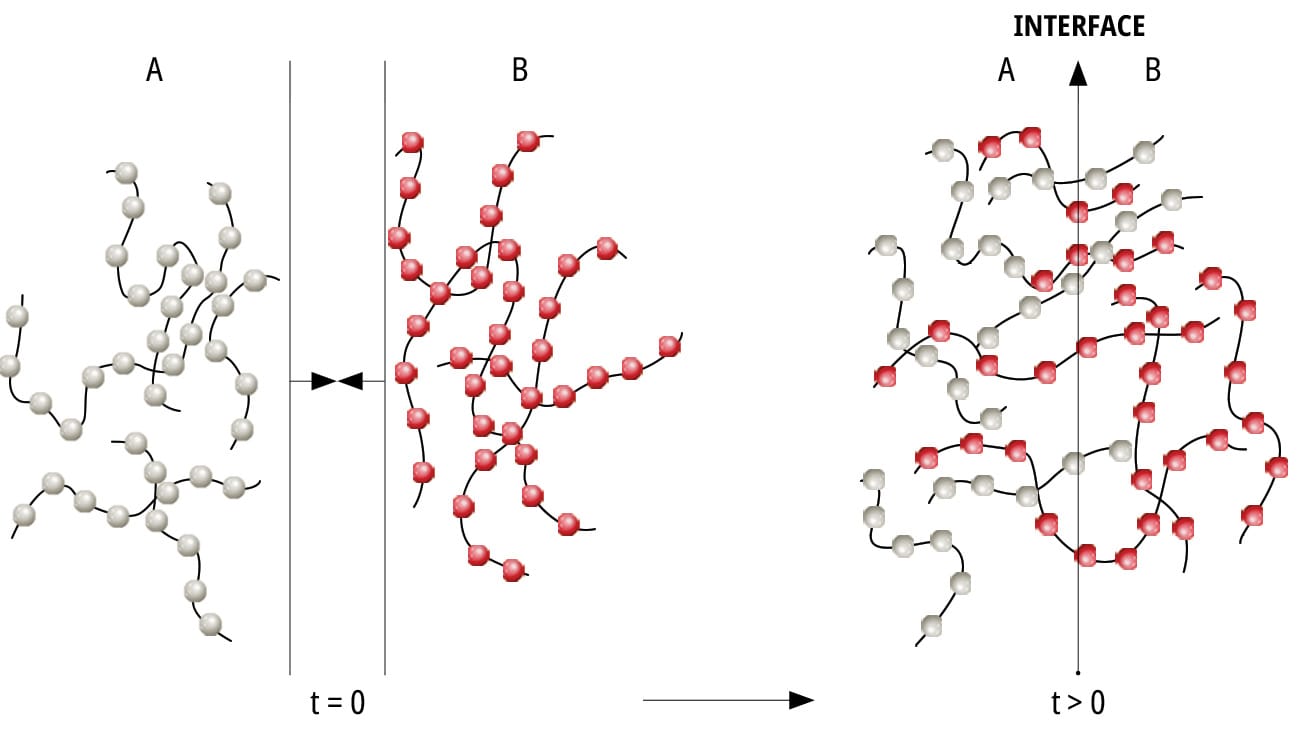
4.1.2 Diffusion Theory
Diffusion theory is applicable for long-chain polymers that are capable of movement. Adhesion is the result of the diffusion of molecules between the adhesive and the surface. Depending on the adhesive’s chemical properties, operational conditions and substrate, the diffusion will vary in depth.