3.1.12 Renewable Energy
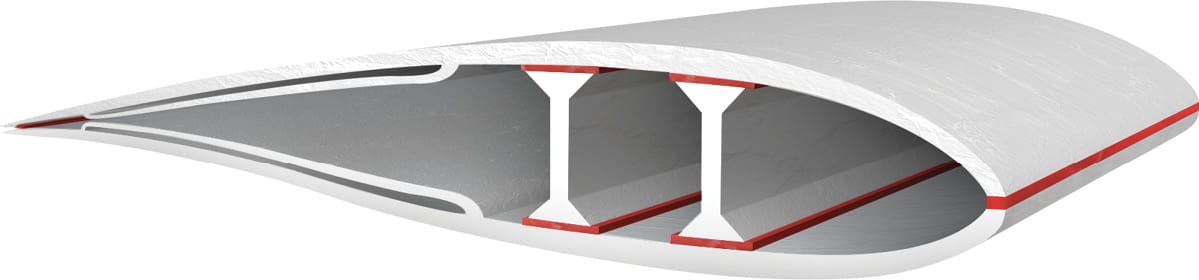
Wind power has developed and evolved in recent years, mainly because of the increased use of adhesives to construct wind turbines. Wind turbines were previously made of galvanised steel, but aluminium and composite materials are now used for their lightweight properties. This material change also reduces the risk of corrosion. Wind turbines can be placed in any environment and are exposed to constant vibrations; this increases the risk of rivets and screws loosening and causing failures. Such failures could cause a major catastrophe: wind turbines are large, and the blades are placed high up and often travel at high speeds. Using adhesives provides better stress distribution over the entire bond area instead of concentrating the stress at each mechanical fastener.
In addition, the use of adhesives makes the rotor blades lighter, providing increased efficiency. Bonding the blades also allows for more aerodynamic designs, further increasing their effectiveness. Carbon-reinforced composites are regularly used for their physical characteristics and compatibility with adhesives. Should rotor blades sustain damage from hitting flying objects, lightning strikes, edge erosion, tip fractures or delamination, the blades are repaired in situ due to the complexity and cost of transporting the blades. Adhesives play a crucial role in repairing the damage because they offer a fast processing speed and versatility that can quickly return the turbine to a serviceable condition.
Solar power is another typical application in the renewable energy sector. Adhesives play a vital role in the development and improvement of photovoltaic cell systems, where their many benefits over traditional joining methods make their use effective. If correctly specified, the ability of an adhesive to join dissimilar materials over a wide temperature range while accommodating static and dynamic loads can be invaluable. The sealing properties of a bonded joint also contribute to the long-term protection and performance of solar power systems. Not only do adhesives allow for greater design freedom, but they also offer less obvious benefits, such as fast processing for emergency repairs or high throughput and outstanding resistance to moisture and UV. Some of the primary adhesive applications within a solar panel include frame bonding and sealing, bonding mirrors and top layers to supports, and insulating electrical components.

