3.1 Evolution of Bonding
3.1.1 incorporating new substances
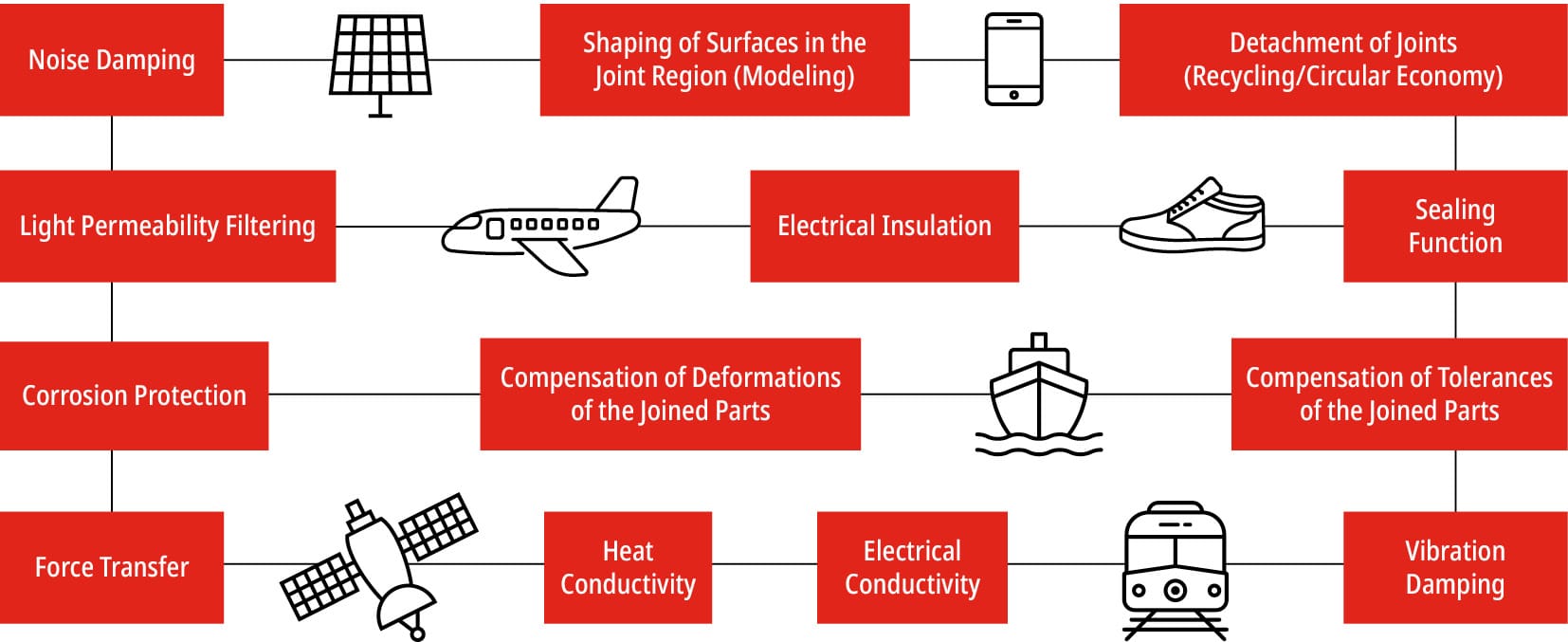
Adhesive bonding is an efficient, economical and durable method for assembling dissimilar materials. It is highly versatile and capable of joining almost all types of materials to themselves and each other. Other joining methods and processes, such as welding and riveting, are limited by material characteristics, joint geometries and application requirements. Bonding is used for many applications, including joining films, sheets, fabrics, sandwich panels, honeycomb cores, sandpaper, cardboard boxes and flocked wallpaper.
An adhesive can compensate for joint tolerance by filling gaps and surface variations, allowing increased flexibility and load transmission. An adhesively bonded joint can also seal against liquids (preventing corrosion of metals) and gases. Many adhesives are based on organic polymers, which are non-conductive and can provide electrical insulation. If this is not desired, metal powder (usually silver) is added to an adhesive to increase its electrical conductivity. These adhesives are commonly used in microelectronics for the transmission of currents. Some adhesives are specially modified for heat transfer and have high or low thermal conductivity.10
10) Brune, Kai & Dieckhoff, Stefan & Fricke, Holger & Groß, Andreas & Haag, Katharina & Hartwig, Andreas & Cavalcanti, Welchy & Mayer, Bernd & Noeske, P.-L & Wilken, Ralph. (2020). Circular Economy and Adhesive Bonding Technology Study by the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM (B. Mayer, A. Groß; eds.). 10.24406/ifam-n-603186.
These properties of adhesives allow dissimilar materials to be joined and combined in endless applications, offering increased design freedom and often enabling fuel and energy savings both in production and during operation.