2.2.5.3 Automation vs Manual Assembly
Determining the most suitable production process is based on multiple parameters. The daily production rate is generally a good starting point.
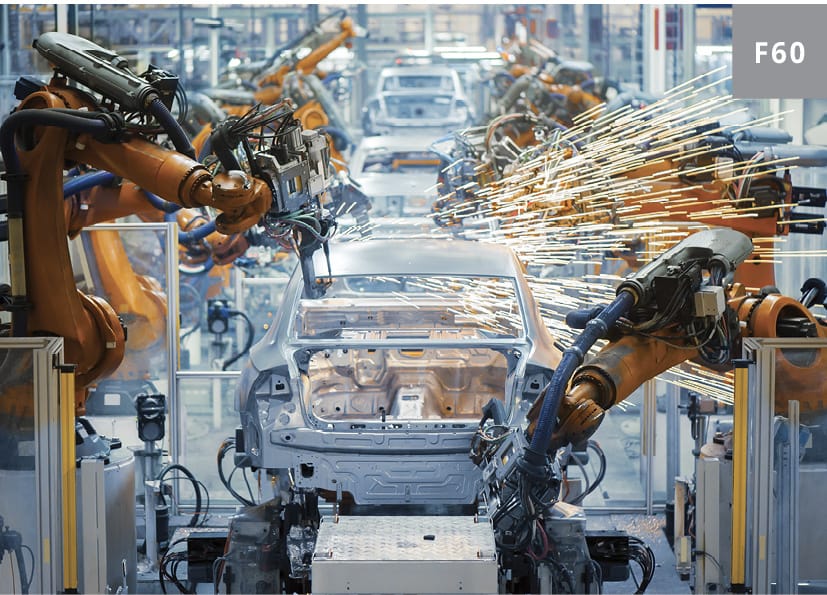
Joining methods should be compatible with automation machines and robots to keep up with the production demands. For example, welding and adhesive bonding can be automated simultaneously on the same production line, while assembling fasteners and adhesive bonding cannot be easily automated.



2.2.5.4 Sealing of the Joint or Assembly
For an assembly to perform effectively, sealing can be critical. Sealing means keeping the environment or media on one side of an assembly and out of the joint. This is important in some situations, as atmospheric moisture can lead to water ingress between joining surfaces and induce corrosion. Keeping fluids inside or outside of an assembly can be a critical requirement for an application, e.g. water storage tanks, filter housings, shipping containers, rail carriages and medical devices. Joining methods such as welding, bonding and brazing are preferred where sealing is required. Fasteners and rivets can be selected if sealing is not a priority.




