2.2.1.1 METAL
A multitude of different metals and their alloys are used to realise every conceivable application. Two of the most commonly used metals are aluminium and steel. For more detailed information regarding metals, see the Loctite® Design Guide for Bonding Metals.
2.2.1.2 Plastic
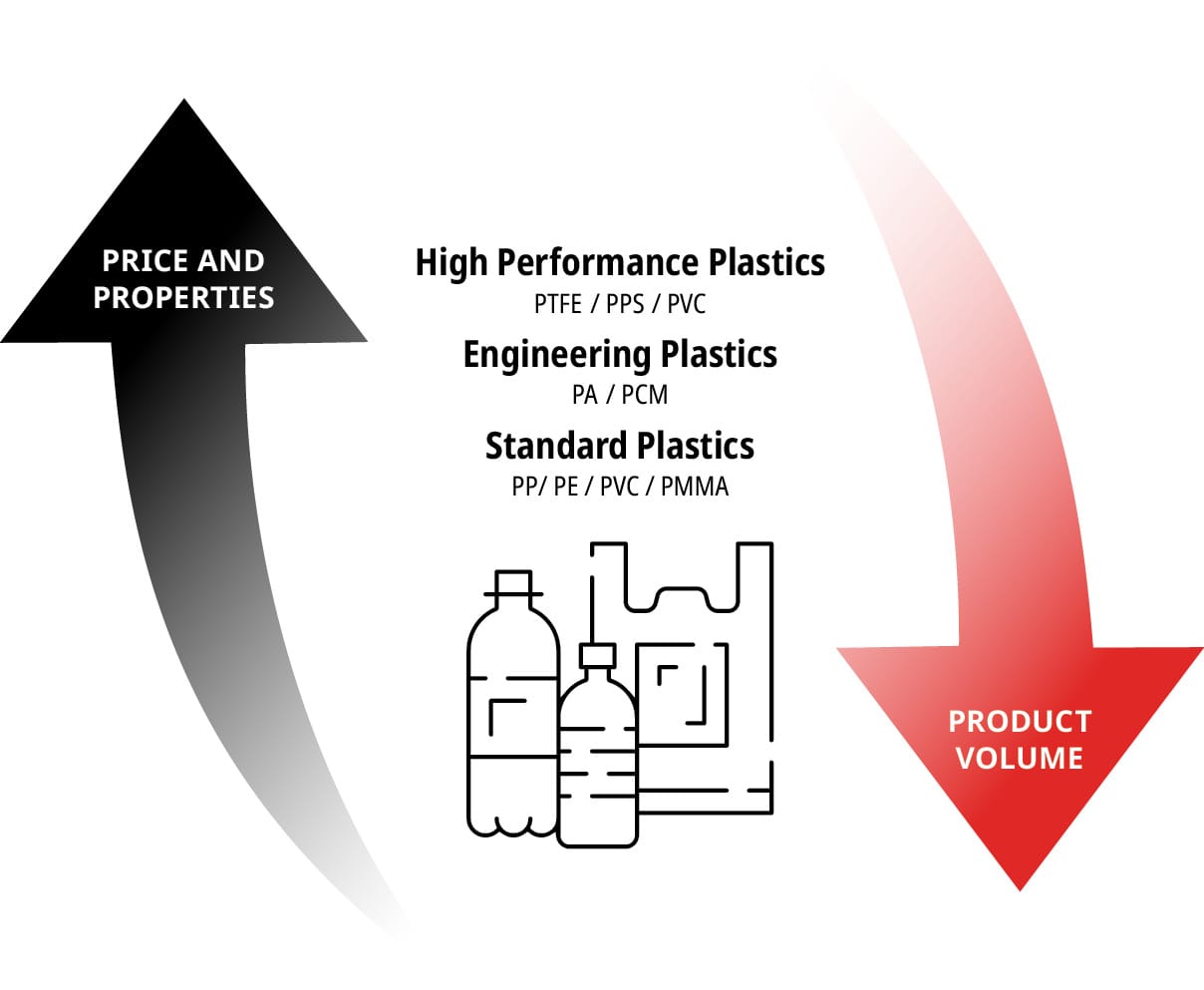
Plastics are becoming increasingly important in industry because of their versatile properties. A plastic (raw material, additives and production) is often selected as the most suitable material for the desired application due to its combination of machinability, hardness, elasticity, tensile and yield strength, temperature and heat resistance, environmental resistance and chemical resistance. An advantage of plastics over metals is their low weight, but they have limitations in mechanical and thermal stability by comparison; for example, very thin films of plastic can be difficult to bond. Figure 20 describes three main groups of plastics – standard plastics, engineering plastics and high-performance plastics – and their core representatives. For more detailed information regarding plastics, see the Loctite Design Guide for Bonding Plastics.